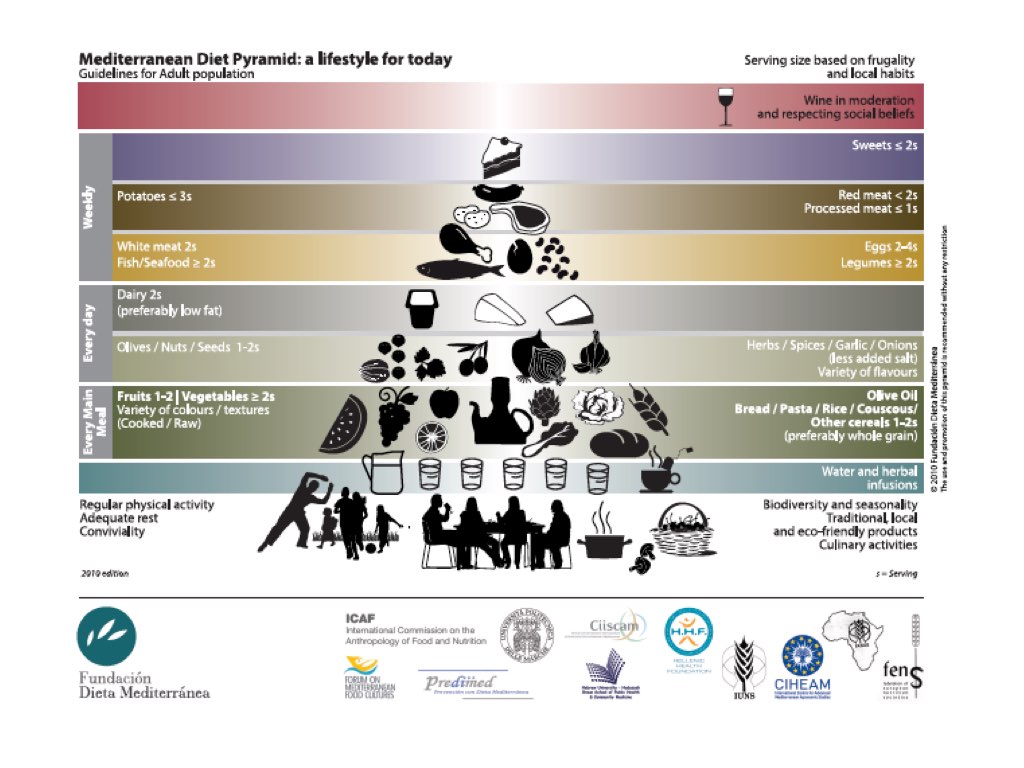
INTRODUCTION
The Mediterranean Diet is a lifestyle with a dietary pattern that has been built from thousands of interactions amongst the different societies and cultures that have lived in the Mediterranean Basin. This eating habit is characterized by seasonal food produced locally and minimally processed rich in high-quality nutrients and bioactive compounds. The Mediterranean Diet promotes a high amount of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole-grain cereals, as well as nuts and seeds. Moreover, olive oil is of the central elements and is used in each daily meal. Furthermore, the Mediterranean Diet also includes a moderate amount of dairy products, eggs, fish, and seafood; meat and processed food are recommended in a lower amount. One of the main features of this eating habit it’s its richness in the use of different spice types for cooking, as well as a moderate amount of wine consumption during the meals.
It is since the Seven Countries Study (SCS) – https://www.sevencountriesstudy.com, led by Ancel Keys and his Italian colleague Flaminio Fidanza, as well as their SCS colleagues, in the ‘60s, they showed together with their colleagues that dietary patterns in the Mediterranean and Japan at that time were associated with low rates of coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality. This was the first major study that investigated diet and lifestyle along with other risk factors for cardiovascular disease by contrasting countries (USA, Finland, Yugoslavia, Netherlands, Italy, Greece, and Japan) and their cultures over an extended period of time (1958 – 1983 (25 years)).
More recently, in 2013, the PREDIMED study – http://www.predimed.es/, led by Dr. Ramón Estruch, with a total of 7447 participants (55 to 80 years of age, 57% women), concluded that among people with high cardiovascular risk, a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil or nuts reduces the incidence of serious cardiovascular events.
If you’re interested in knowing your adherence to the Mediterranean Diet pattern, take up this 14 short questions test based on the PREDIMED test used during the study.
Quick Mediterranean Diet Test.
HEALTH BENEFITS
There is scientific evidence that a traditional Mediterranean diet consisting of large amounts of fresh and seasonal fruits and vegetables, nuts, fish, dairy products, virgin olive oil, and a moderate amount of red wine – coupled with physical activity – can reduce the risk of serious mental and physical health problems by:
Increasing your life expectancy and reducing mortality rates
Several studies have evaluated the effects of high adherence to the traditional Mediterranean diet on life expectancy and, consequently, to all-cause mortality and mortality due to specific causes. For example, the second phase of the Seven Country Study already observed significantly lower mortality due to cardiovascular disease in Greece compared to the mortality observed in the USA or Finland in the ‘60s.
Reducing obesity and overweight and helping to maintain a healthy weight
Obesity is a key risk factor for morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease and the development of type 2 diabetes, some types of cancers, and other disorders.
The standard recommendation for the prevention and treatment of obesity/overweight is restricting (or reducing drastically) dietary energy intake and increasing physical activity. Fat in food is high in kcal (energy) and there is a persistent belief that increased dietary fat intake will lead to weight gain, whereas reduced fat intake will promote weight loss. The intake of both olive oil and nuts, as part of the Mediterranean Diet, are categorized as healthy fats because they have been associated with the prevention of cardiovascular disease and weight loss compared to processed fats.
Preventing cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease continues to be the main cause of death worldwide. The PREDIMED study concluded that a Mediterranean Diet supplemented with either extra-virgin olive oil or nuts was associated with a 30% relative reduction in major cardiovascular events, i.e. the risk to suffer from health problems was 30% lower in the people that intake those foods compared to the ones who didn’t.
Preventing and controlling type 2 diabetes
Mediterranean diets are rich in fruit, vegetables, and whole grains and are widely known to be healthy for people with type 2 diabetes. Many studies have proven its protective effect over this disease because it can help diabetics control their blood sugar levels more efficiently, especially for its high amount of natural fiber.
Preventing certain types of cancer
Higher adherence to Mediterranean Diet has been associated with lower cancer mortality, especially for colorectal cancer.
Reducing mental health problems
Data increasingly has shown that some dietary patterns are connected with reduced prevalence and reduced risk of psychiatric illness, mainly anxiety and depression, but also including bipolar disorders, Alzheimer and Parkinson’s disease. Studies carried out in recent years also indicate that dietary interventions in patients with depression may constitute an effective and accessible treatment strategy against this disease. Thus, a healthy diet such as the Mediterranean diet may help to prevent and even to improve psychiatric disorders.